
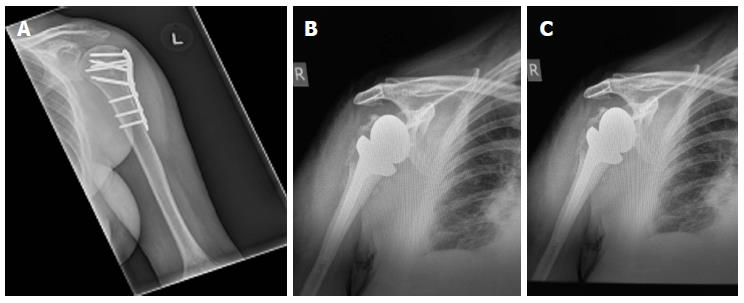
If left untreated, these fractures can cause subscapularis muscle (stabilizer and mobilizer muscle) deficiency and require a major muscle transfer procedure. Lesser tuberosity fractures: These fractures are often caused by posterior shoulder dislocations or traumatic muscle contractions by electrical shock or convulsions. Partial rotator cuff tears often accompany non-displaced fractures and these fractures can be diagnosed using MRI or diagnostic arthroscopy. Direct impact on the shoulder causes the tuberosity bone to break into multiple fragments. A fragment of the greater tuberosity is pulled off when the cuff muscle contracts or the anterior shoulder dislocates. Greater tuberosity fractures: Greater tuberosity fractures are less common and are seen in cases of shoulder dislocations and in those with osteoporosis. These fractures also damage the axillary nerve that carries sensory information from the shoulder. Surgical neck fractures: Fractures of the surgical neck are most common in osteoporotic bone. While mild trauma can break humeral head in the elderly, a more significant trauma results in its fracture in the young.
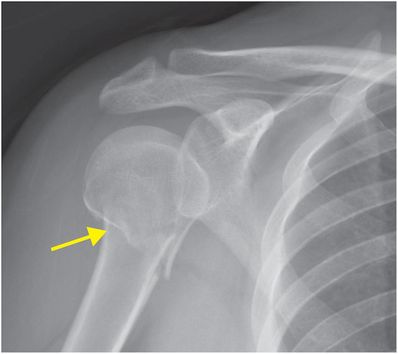
Humeral head fractures: Humeral head fractures very often occur in elderly individuals and chances are more in those with osteoporotic bone. Proximal humerus fractures can be categorized into 4 groups: In younger individuals, a severe trauma such as a fall from a height on an outstretched hand or motor vehicle accident can cause these fractures. Causes of Proximal Humerus Fracturesįractures of the proximal humerus are common in elderly individuals suffering from osteoporosis. Just below the head are two processes called the greater and lesser tubercles, which form the sites of attachment for the rotator cuff muscles. The humerus is broadly divided into the head, neck and shaft region. The proximal humerus is the upper end of the arm bone that forms the shoulder joint. It articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula (shoulder blade) to form the shoulder joint and with the lower arm bones – the ulna and radius – to form the elbow joint. The humerus is the bone that forms the upper arm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
